Bib
Examples
Basics
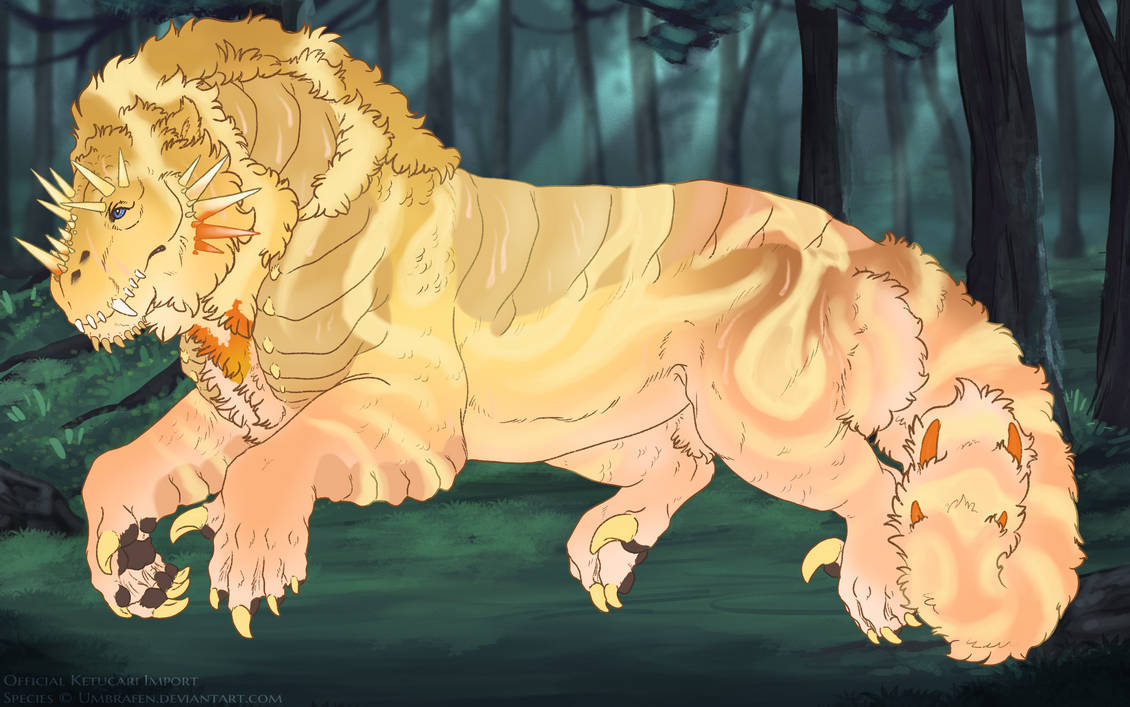
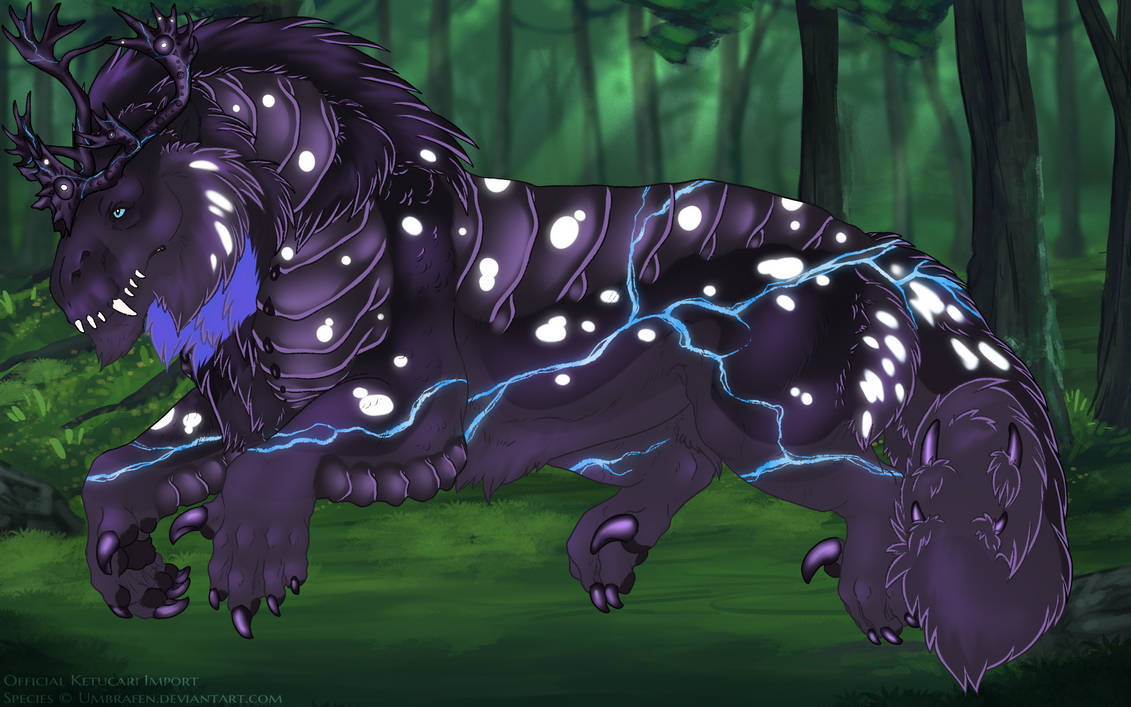
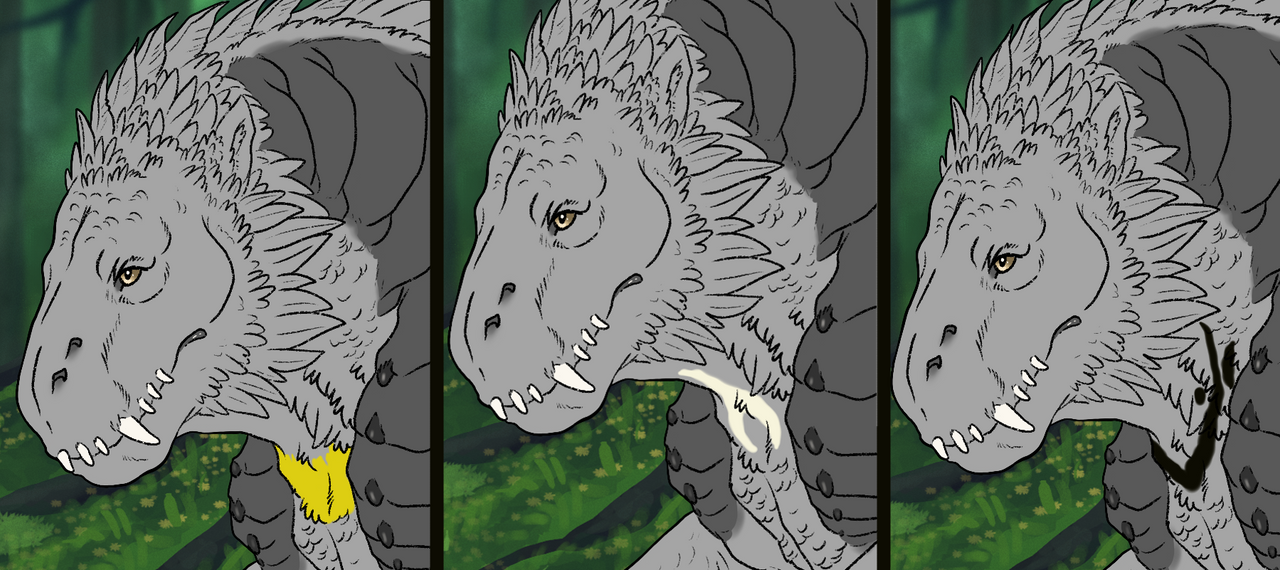
- Bib creates a small colorful patch on the ketucari’s throat.
- In your ketucari's genotype, bib is denoted by the letters "nBi" (heterozygous) or "BiBi" (homozygous).
- In its heterozygous form, bib has a pass rate of 45%. Homozygous bib has a 70% pass rate.
Color and Shape
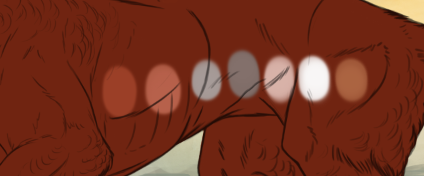
The base of bib can be a lighter or darker color of your chosen base, with a minor deviation in hue, or any highly saturated color (greater than 180 saturation).
If a saturated color, Bib may gradient to second color. If lighter/darker than the base coat it may also have a slight gradient. It can also be a fully desaturated color of the base. Bib may never be pure white* or pure black**.
(*unless on a white ketucari)
(**unless on a charcoal ketucari)
A small sample of acceptable colors for Colored Bib
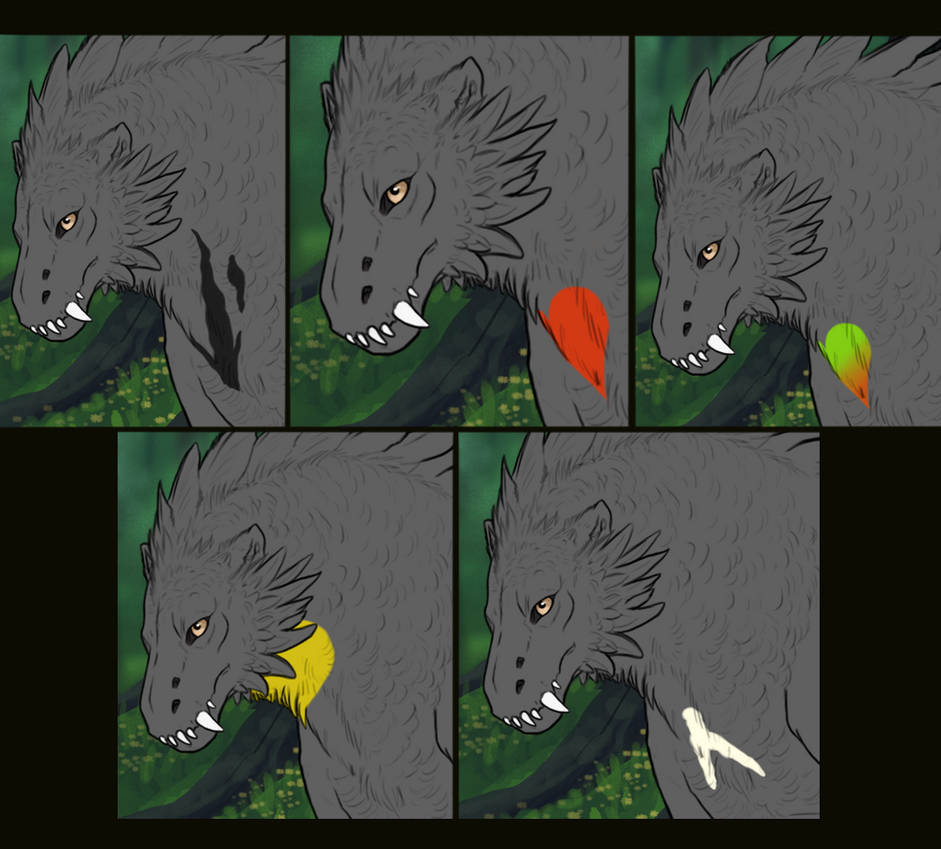
Within its range it may be any symmetrical shape, natural or unnatural. It may have soft edges, but not fully blended out. It may be broken up.
[Insert shape examples]
Range
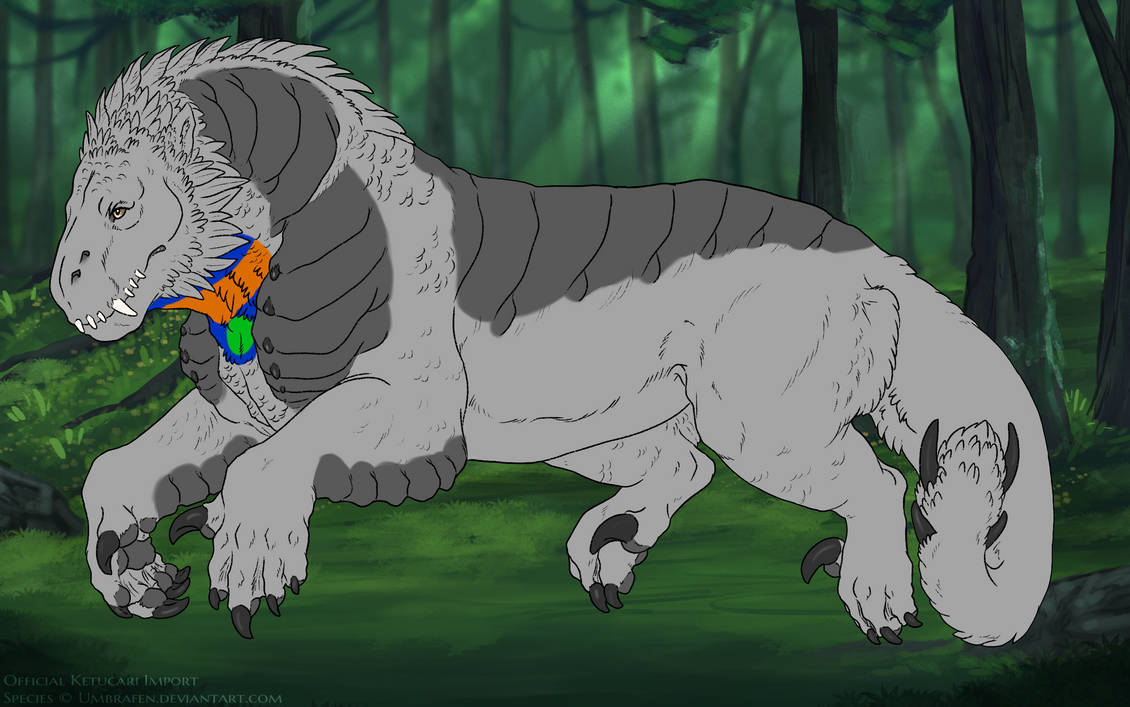
Bib covers the throat of the ketucari. Visually, on a smooth ketucari, this would be from the third cheek feather up, to the front of the shoulder. It does not extend onto the chest.
Bib may only cover up to one third of its total range:
In the following guides, green is the minimum range for bib, orange the maximum, and blue all the areas it can appear.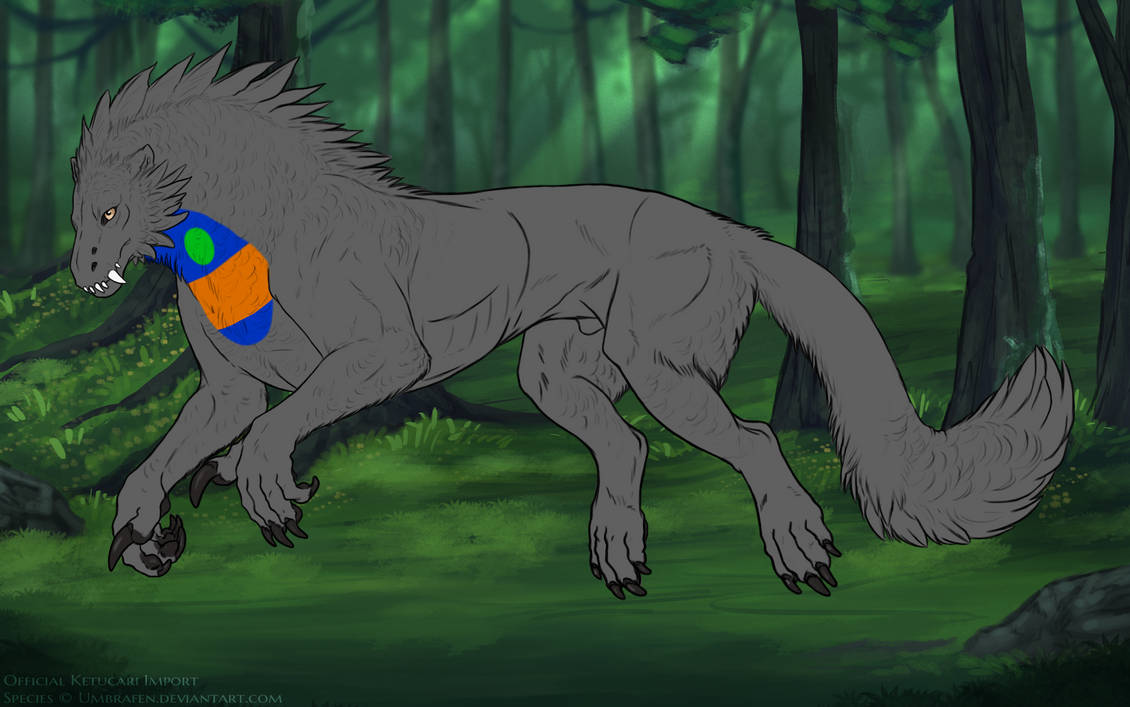
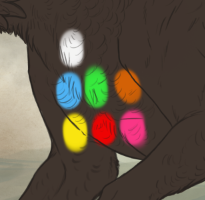
Below are a small sample of the sorts of shapes Bib can create!
Interaction With Other Markings
- Bib must go over Hood if both are present.
- Bib may alternatively combine with Hood to erase the top or lower half of Hood’s range.
- If Bib and Morpho are on the same geno, Bib may adopt Morpho’s color rules. This does not count as restricting Morpho to a gene.
- On a dilute ketucari, “bright” bib can be creamier colors, allowing for saturation to start at 50.